For organizations with multiple online accounts, tightening company security should be a top priority to prevent data breaches or theft. The first step to avoiding a data breach is creating unique passwords for your accounts.
But suppose you’re like many people who resort to reusing their old passwords to create new accounts. In that case, it’s safe to say that it’s only a matter of time before your data and online accounts are compromised. And by extension, once your overused passwords are discovered, all the accounts associated with them are at risk.
SEE: Keeper Password Manager Review: Features, Pros & Cons (TechRepublic)
One way to solve this problem is through password managers — tools that help you generate unique, secure, complex passwords and store them in a vault for easy access. Password managers secure account credentials, making them difficult to hack.
Here is a guide to how password managers work and how you can choose the best one to tighten your company’s online security.
What is a password manager?
A password manager is a tool that helps you generate, store and manage passwords or credentials online. It uses encryption to protect the stored credentials and allows you to retrieve them using a master password. The idea behind this technology is to enhance security by promoting the use of unique, strong passwords for different services. This helps reduce the risk associated with password reuse and simplifies the process of managing multiple login credentials.
How do password managers work?
While many browsers feature a basic password manager, only a top-tier third-party password management application can offer you robust security and convenience through features like password generation, VPN, dark web monitoring, encryption and two-factor authentication.
While you can simply add password managers to your browsers as an extension, the first step to using many password managers is installing the client on your computer or mobile device.
To install a password manager on your mobile or desktop, follow these simple steps:
- Download the password manager program.
- Open the app and create a master password for your vault.
- Add the password manager extension to your browser.
- Log into your accounts.
- Change your existing passwords.
When your password manager is active, instead of manually entering the password on websites, the password manager, through the extension, prompts you to input your master password to access your unique passwords. This master password serves as the key to unlocking the encrypted vault containing all stored passwords. If you have already logged into the password manager, it seamlessly auto-fills the required login information on the website, sparing you the need to recall individual details.
If you want an in-depth video explanation on password managers, we’ve got you covered. Check out our Password Managers 101 video feature on the official TechRepublic YouTube channel that’s available to view right now.
In this video, we look into the features and benefits of password managers, how safe password managers are to use and who should invest in password manager solutions in the first place.
Types of password managers
While different password management solutions serve similar functions, their key features and modes of operation distinguish them. Below are three popular categories that can be valuable for your organization.
Locally installed or offline password managers
These are desktop-based password management solutions that store your passwords directly on your device, such as a laptop. These passwords are typically secured within an encrypted vault, enhancing the security of your sensitive information.
Unlike cloud-based alternatives, locally installed password managers do not rely on external servers to store or manage your passwords. The advantage here is that your passwords are not accessible from any other device unless they have been synchronized with the device. This local storage approach provides you with a high level of control and privacy if you prefer to keep your data away from public networks.
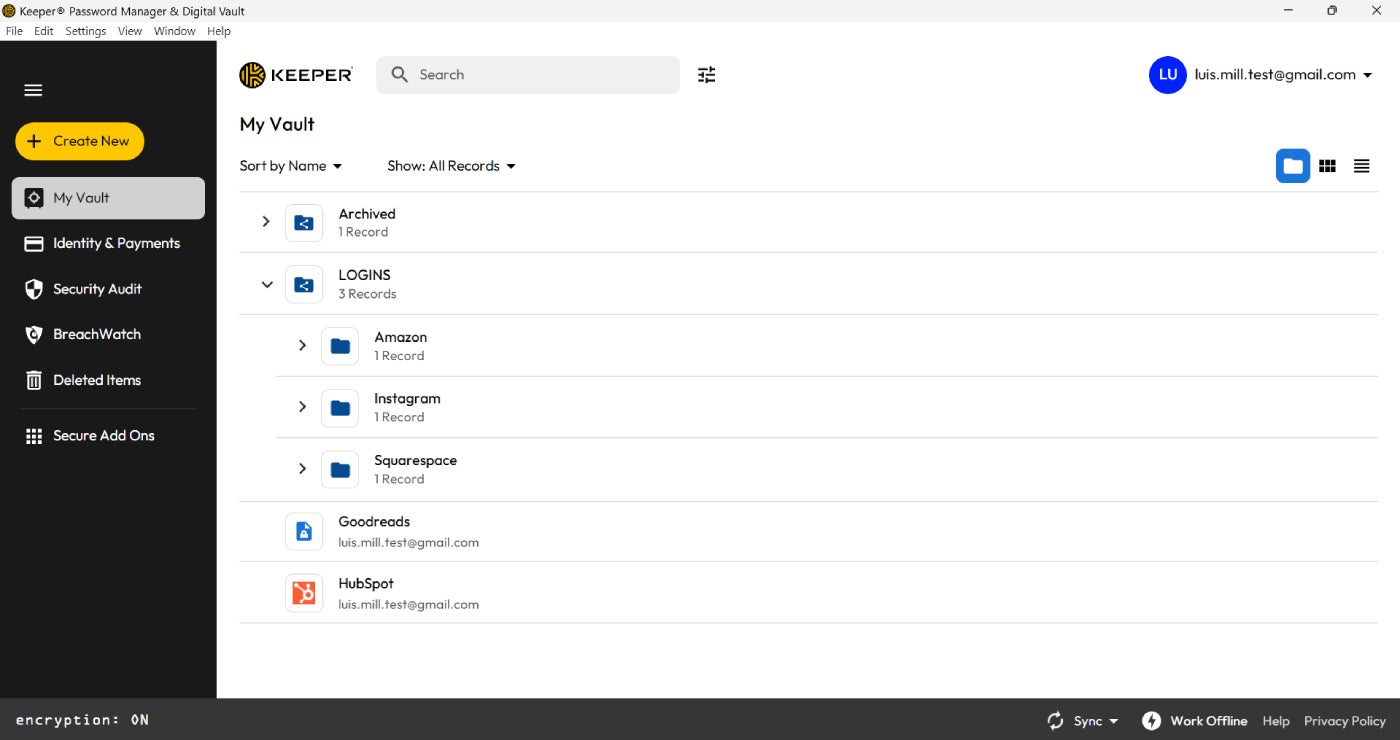
Popular examples of offline password managers are KeePass and Enpass. Both password managers allow users to store their credentials directly on their machine, without having them synced or stored on the cloud.
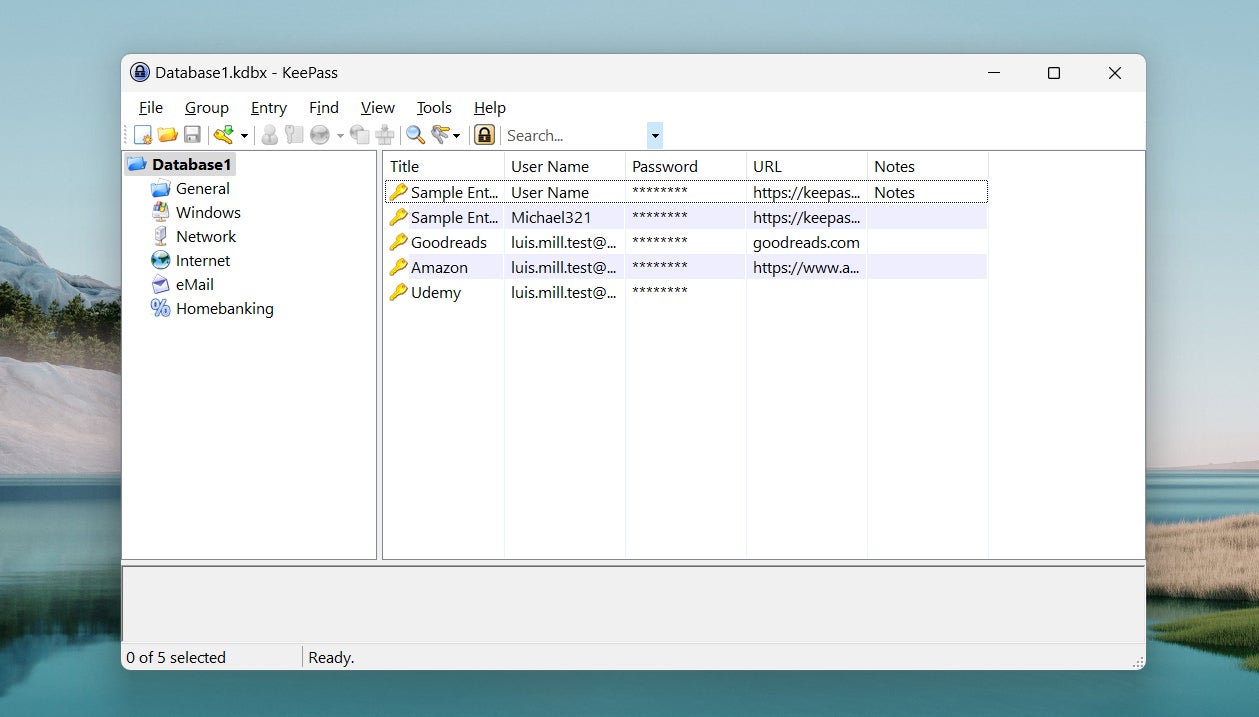
However, it comes with a trade-off: If you were to lose the device where the password manager is installed, you would also lose access to all the stored passwords.
Some password managers, like 1Password, Keeper and Dashlane attempt to strike a balance between privacy and convenience by offering features that allow you to create multiple password vaults across your devices. These vaults can be synchronized when you connect to the internet. This enables a certain degree of flexibility while still maintaining a primarily offline storage approach. This way, you can benefit from the convenience of syncing your passwords across devices without entirely relying on external servers for data storage.
Web-based or online password manager services
These password managers operate on a cloud-based model, where encrypted passwords are stored on the service provider’s network. In this context, the service provider assumes direct responsibility for the security of your passwords.
Programs like 1Password and NordPass exemplify cloud-based password managers. The key advantage of these services lies in their accessibility — you can reach your password vaults from any device with an internet connection.
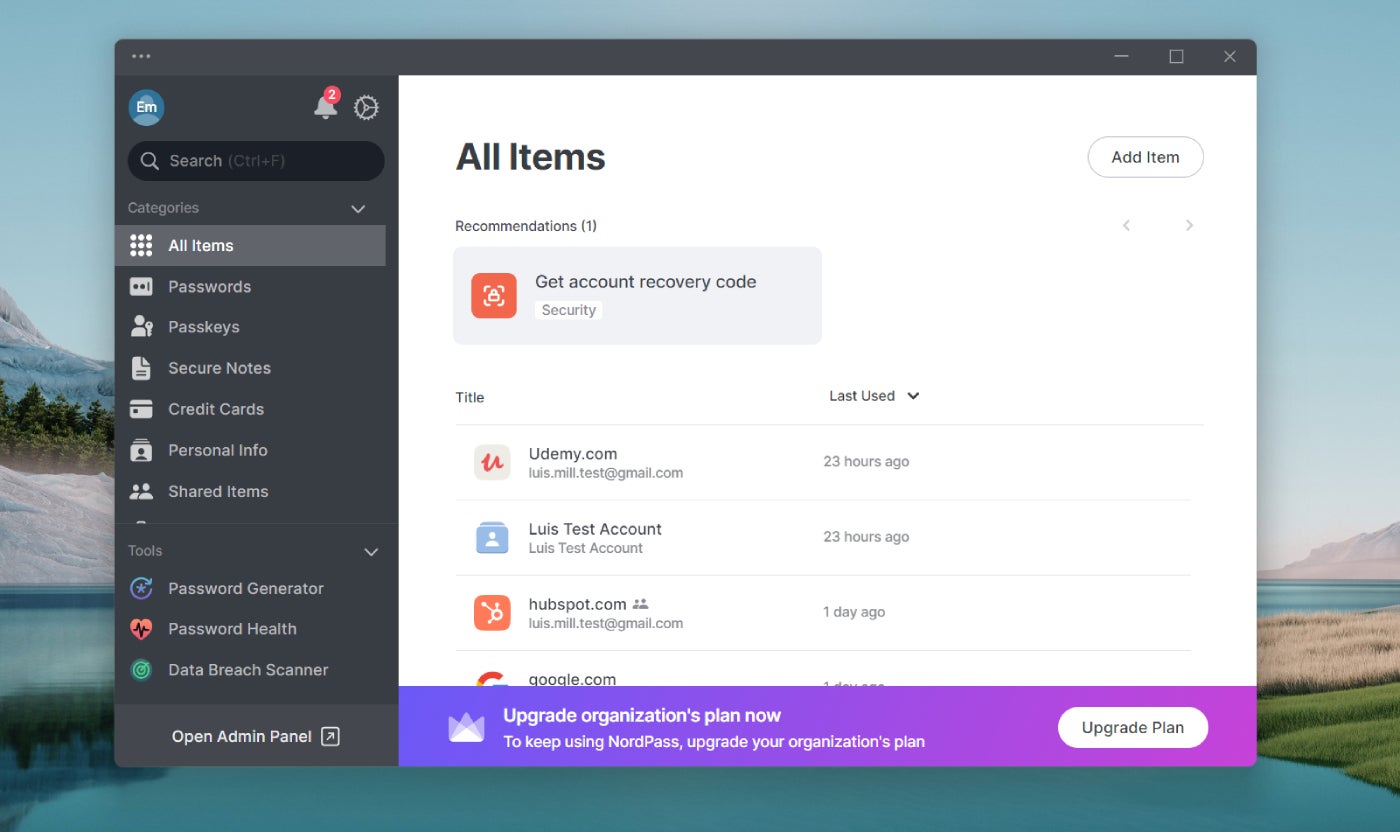
Web-based password managers typically come in various forms, commonly as browser extensions, desktop applications or mobile apps.
Stateless or token-based password managers
Stateless or token-based password managers differ from traditional password managers in that they do not store passwords directly. Instead, they generate a unique password for each website or service based on a master password and a site-specific identifier known as a token. This token can be a physical device, such as a USB key, or a code generated by a mobile app. When you log in to a website, the password manager generates a new password based on the current master password and the site’s token.
Examples of token-based password managers are YubiKey, OnlyKey and Google Titan Security Key. This token-based approach is prevalent in cryptocurrency security and is reminiscent of specific online banking login methods that require physical devices.
The absence of a fixed password on the device enhances security, making it challenging for hackers to obtain login credentials even if they compromise your account. However, reliance on a physical device exposes you to the risk of losing access if the device is lost or damaged.
Why your organization needs a password manager
Your organization needs a password manager to ensure centralized control and visibility over your employees’ password practices. Without it, tracking and managing passwords become challenging. Implementing a password manager facilitates seamless onboarding and offboarding processes. This strengthens overall security and efficiency within your business.
Password managers provide the following for organizations:
Added protection with password generators
Password managers offer enhanced security for organizations by incorporating password generators. With this feature, you can generate strong, unique passwords for each user in your organization, thereby minimizing the risk of unauthorized access to your important data.
Improves log-in experience
You can use a password manager to streamline the login process for your organization, especially if you have a remote or hybrid work setup. For example, 1Password, LastPass and many other password management solutions have the capability to securely store and auto-fill your credentials across different platforms. This feature improves user convenience while maintaining security standards.
Works across multiple devices
Today, most password managers are cloud-based and the advantage of this is the convenience of accessing stored credentials across multiple devices, like smartphones, PCs or desktops. Your employees will have the flexibility and ease of logging in to work from their various devices without the need to log in from a single localized device.
Secure password sharing
Another important feature of a password manager is the ability to facilitate secure password sharing within your organization, allowing your team to collaborate without compromising security. You can control who has access to sensitive information while still promoting efficient teamwork.
Multi-factor authentication
Most password managers integrate multi-factor authentication into their security checks, which adds an extra layer of protection for your company information. One significant advantage of this feature is that it reduces the risk of unauthorized access and safeguards confidential information from potential hackers.
Choosing the best password manager for your company
Choosing a good password manager for your company is the first step to securing your systems and sensitive data. Here are the factors to consider when choosing the best password manager for your company:
Pricing
Most password managers offer tiered pricing, typically ranging from $1 up to $20 per user per month, with variations in features and storage. However, there are still many options available on the market with forever free and feature scale-up modes.
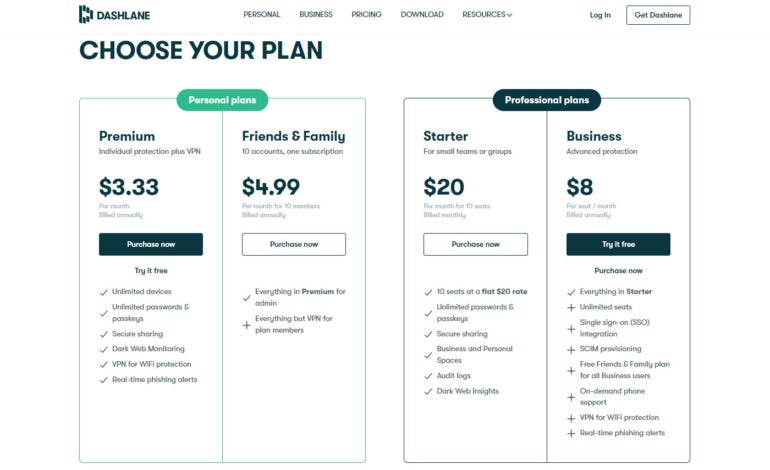
For example, Bitwarden and LastPass offer free plans to start with. Consider the size of your company and specific needs when evaluating packages to ensure scalability without unnecessary features. It’s always better to use trials to understand how the program works before making any financial commitments.
Stand-out capabilities
Advanced features like secure password sharing, 2FA support and integration with other tools are becoming standard. Notable options like Dashlane and 1Password often offer well-structured plans that include 2FA.
So, prioritize capabilities that align with your company’s workflow and security requirements. For example, if your employees are remote-based, then you have to make sure secure password sharing is included in your selection.
Technical support
24/7 customer support via email, chat or phone is a standard offering available with most password managers. Evaluate the responsiveness and expertise of the support team as quick assistance can be critical in case of any issues or security concerns.
User interface and experience
Intuitive interfaces for both administrators and end-users are factors you shouldn’t swerve under the rug. Test the user experience to ensure ease of use.

It should have a user-friendly design featuring an intuitive interface for swift password generation, storage and management as this can impact adoption rates and overall security compliance within the company.
Auditing and reporting features
Robust auditing tools for tracking user activity and generating reports on password hygiene should be included in any good password management solution. It is crucial to have a complete record of who accessed the application, what resources were assessed and when they were assessed, along with information about every single action performed by the users within the application.
Mobile device support
Password managers should have dedicated mobile apps with secure synchronization across devices. Test the mobile experience to ensure usability without compromising security, especially for employees who frequently work on the go.
Backup and recovery options
Regular backups and a reliable recovery process for encrypted data are essential features any good password management application should possess. Assess the backup frequency, methods and recovery options of any solution you choose. This is to minimize the risk of data loss and ensure business continuity.
Compliance and certifications
Password managers should comply with data protection regulations and may hold certifications like SOC 2 or ISO 27001. Adopting ISO 27001 provides a comprehensive approach to information security. So, verify that any password manager you choose complies with relevant industry standards to protect sensitive company information.
Recommended password managers
While there are many password managers out there, not all of them offer the same levels of security and convenience. Below are the top 3 business password managers to consider:
1Password: Best for comprehensive security features

1Password offers many features for both individual and business users. Some notable features include single sign-on, 2FA, end-to-end encryption, breach alerts, dark web monitoring and several others. If you are a business owner and want to manage multiple accounts, collaborate with teams and securely share sensitive data, then this password manager is your ideal choice. It can work on Chrome, Safari, Edge, Firefox, Brave, macOS, Windows, Linux, iOS and Android browsers and systems. It has a 14-day free trial, and the pricing plan starts at $2.99 for individuals and $7.99 for businesses.
Read our full 1Password review here.
Bitwarden: Best for businesses on a budget

Bitwarden offers an excellent option for small businesses in need of a secure and budget-friendly password manager. Its open-source design and transparent security model ensure a cost-effective solution without sacrificing essential features. It has a free plan and a paid plan that starts at $1 per user/month for individuals and $6 per user/month for enterprises.
Read our full Bitwarden review here.
Dashlane: Best for quality VPN and live dark web monitoring

Dashlane surpasses many competitors with its extensive array of features. It excels in fundamental password management functions, offering top-tier security and easy auto-saving and auto-filling across various operating systems, browsers and devices. It also distinguishes itself with exceptional extras like a high-quality VPN and live dark web monitoring. Its pricing plan starts at $4.99 per user/month for individuals and $8 per user/month for businesses.
Read our full Dashlane review here.


